Your Location:Home > Products > Pharmaceutical intemmediates > Potassium thiocyanate
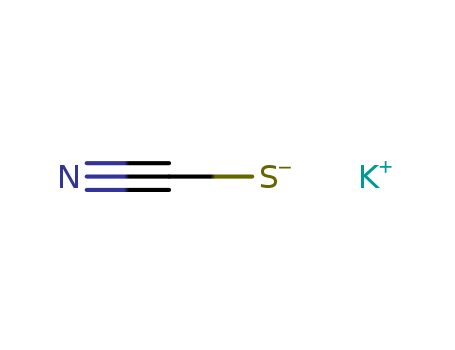
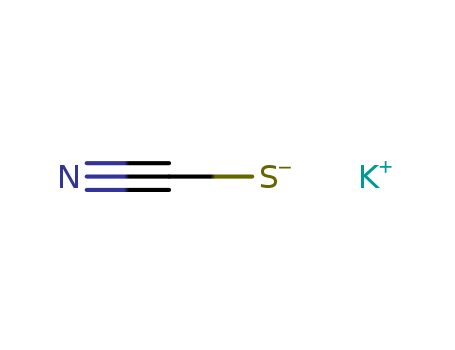
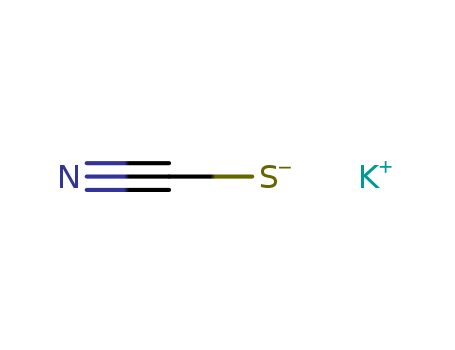
CasNo: 333-20-0
MF: KCNS
Appearance: white crystalline powder
|
Chemical Description |
Potassium thiocyanate and ammonium thiocyanate are both salts that are used in various chemical reactions. |
|
Outline |
Potassium thiocyanate, molecular formula is KSCN, it is also known as KSCN, English is Potassium Thiocyanate, it is colorless monoclinic crystal. The relative density is 1.886. Melting point is about 172.3 ℃. It is soluble in water and it can cool because of the absorption of heat, it is also soluble in alcohol (ethanol) and acetone. Crystalline hemihydrate (KSCN.0.5H2O) can be obtained at low temperature, it is steady at-29-6.8℃, and it can turn blue when be broiled at about 430℃, but it then re-becomes colorless when be colded. When be heated to 500℃, it can decompose. The blood red ferric thiocyanate complex ion FeSCN2 + (iron thiocyanate) can generate in case of Fe3 + (ferric), which is the sensitive method to test the Fe3 + ion, the method can eliminate the influence of all other known metal ions. And it can not react with ferrous salts. It is hygroscopic, and it should be sealed. It has low toxicity. But potassium cyanate is highly toxic substances, the country has limited its production. |
|
Solubility in water (g / 100ml) |
The grams which dissolved in per 100 ml of water at different temperatures (℃) : 177g/0 ℃; 198g/10 ℃; 224g/20 ℃; 255g/30 ℃; 289g/40 ℃ 372g/60 ℃; 492g/80 ℃; 571g/90 ℃; 675g/100 ℃ |
|
Production method |
The mothod of ammonium thiocyanate transformation which is the pressurized synthesis reaction of carbon disulfide and ammonia can generate ammonium thiocyanate and the by-product is ammonium hydrosulfide, and then by desulfurization, ammonium hydrosulfide can evaporate and remove which is decomposed into hydrogen sulfide, when potassium carbonate solution is added into the temperature of 105℃ liquid, it can generates potassium thiocyanate. The reaction process will produce large amount of carbon dioxide and ammonia. Ammonia is recyclable, the reaction solution is filtered to remove insoluble material, and then reduction vaporization is proceeded, and then cooling and crystallization, centrifugal separation is proceeded to obtain industrial potassium thiocyanate. CS2 + 3NH3 → NH4SCN + NH4HS NH4HS → NH3 ↑ + H2S ↑ 2NH4SCN + K2CO3 → 2KSCN + (NH4) 2CO3 (NH4) 2CO3 → 2NH3 ↑ + CO2 ↑ + H2O |
|
Preparation |
Potassium thiocyanate may be made by adding caustic potash to a solution of ammonium thiocyanate, followed by evaporation of the solution. NH4SCN + KOH →KSCN + NH4OHAlso, the compound can be prepared by heating potassium cyanide with sulfur:KCN + S →KSCN. |
|
Hazard |
Toxic by ingestion. |
|
Flammability and Explosibility |
Nonflammable |
|
Safety Profile |
A human poison by ingestion. Poison experimentally by intravenous route. An experimental teratogen. Moderately toxic by subcutaneous and ingestion routes. Large doses can cause slun eruptions, psychoses, and collapse. Incompatible with calcium chlorite and perchloryl fluoride. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of CN-, K2O, SOx, and NOx. See also THIOCYANATES. |
|
Purification Methods |
Crystallise it from H2O if much chloride ion is present in the salt, otherwise from EtOH or MeOH (optionally by addition of Et2O). Filter off on a Büchner funnel without paper, and dry it in a desiccator at room temperature before heating for 1hour at 150o, with a final 10-20minutes at 200o to remove the last traces of solvent [Kolthoff & Lingane J Am Chem Soc 57 126 1935]. Store it in the dark. |
|
Chemical properties |
It is colorless monoclinic crystal. It is soluble in water, and it can cool because of the absorption of heat. It is also soluble in alcohol and acetone. The above information is edited by the lookchem of Wang Xiaodong. |
|
Physical properties |
Colorless rhombohedral crystals; deliquesces; density 1.886 g/cm3at 15°C;melts at 173.2°C, the color of the fused salt changing from brown to green and then blue; turns white again on cooling; decomposes at about 500°C; very soluble in water, 177 g/100mL at 0°C and 217 g/100mL at 20°C; solution cools upon dissolution; aqueous solution neutral; readily dissolves in acetone and liquid ammonia; moderately soluble in hot alcohol. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: A potassium salt which is the monopotassium salt of thiocyanic acid. |
|
General Description |
Potassium thiocyanate is an inorganic potassium salt. Phase transitions in potassium thiocyanate (KSCN) have been investigated by X-ray diffraction studies. The order-disorder type transition with respect to the orientation of the thiocyanate ions was identified. Its polarized infrared spectrum has been reported. It participates in the ring-opening of aziridines. The reaction was carried out in the presence of sulfated zirconia to afford the corresponding β-aminothiocyanates. |
InChI:InChI=1/CNS.K/c2-1-3;/q-1;+1
Dimethyl trisulfide (DMTS) antidote comp...
(Chemical Equation Presented) Label-enab...
We present experimental and theoretical ...
-
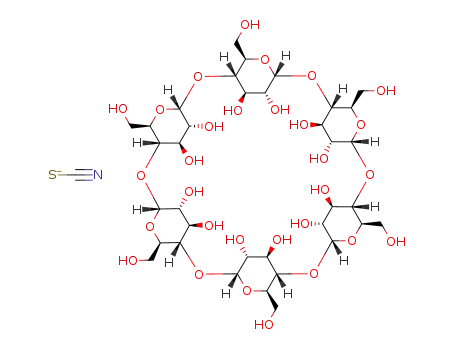
C36H60O30*CNS(1-)

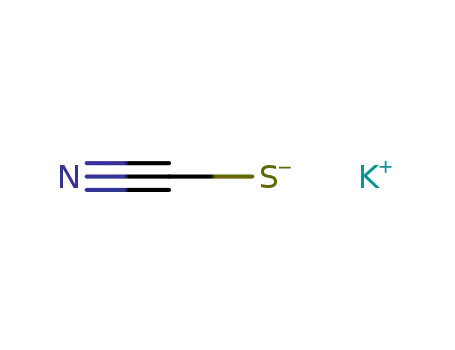
potassium thioacyanate
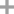
alpha cyclodextrin
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
In water; at 25 ℃; Equilibrium constant; Thermodynamic data; partial molal volume change, atmospheric pressure;
|
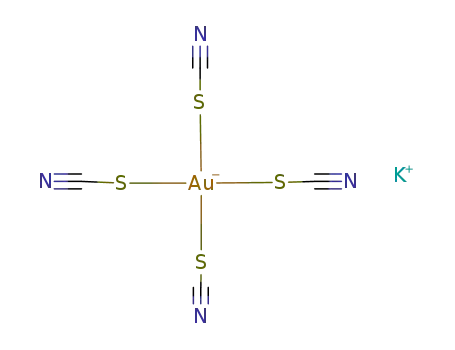
potassium tetrarhodanoaurate(III)

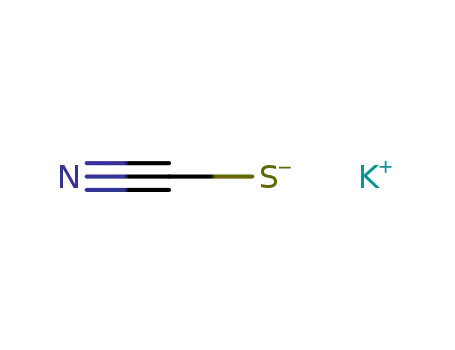
potassium thioacyanate

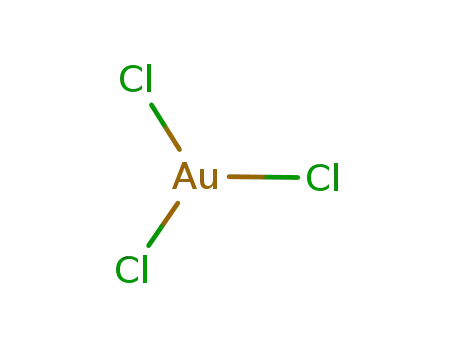
gold(III) chloride
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
decompn. over 100°C;
|
|
|
decompn. over 100°C;
|
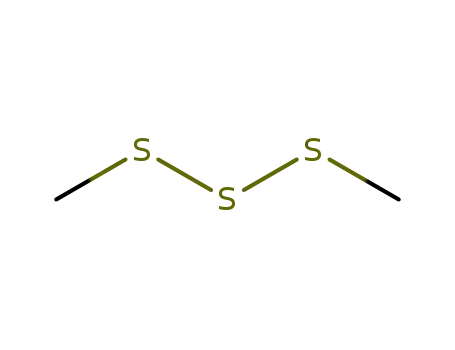
dimethyltrisulfane
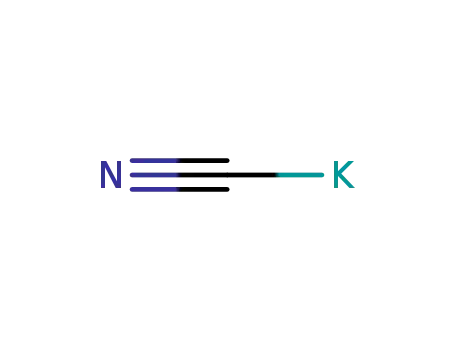
potassium cyanide
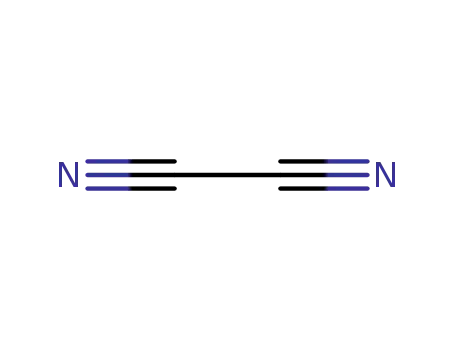
ethanedinitrile
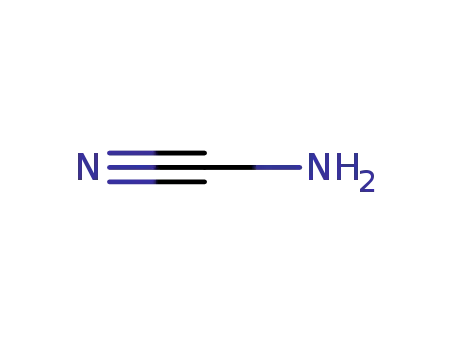
CYANAMID
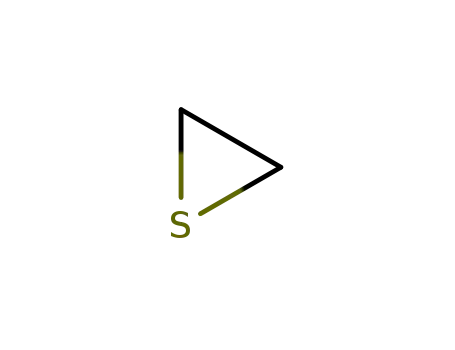
thirane
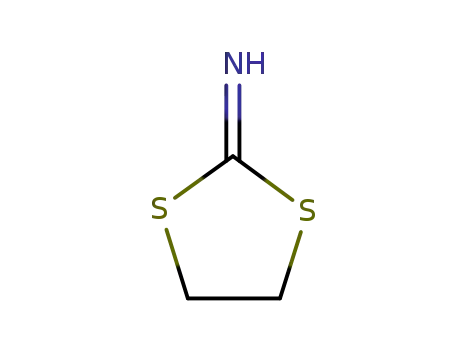
2-imino-1,3-dithiolane
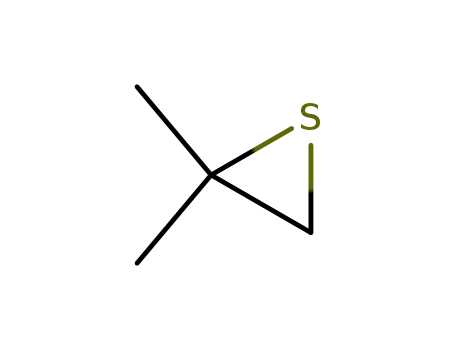
2,2-dimethylthiirane
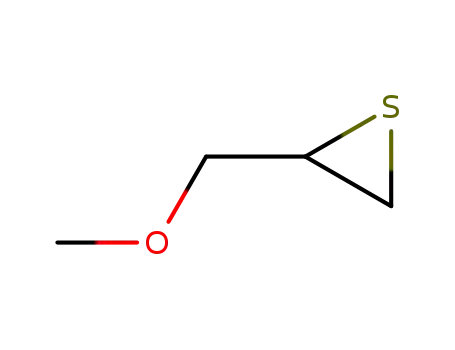
1,2-epithio-3-methoxypropane