Your Location:Home > Products > Food Additives > L-Proline
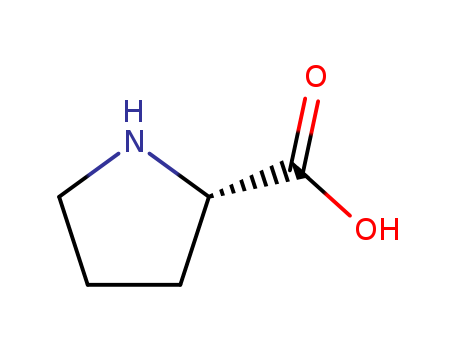


CasNo: 147-85-3
MF: C5H9NO2
Appearance: White crystalline powder
|
Chemical Description |
L-proline serves as the starting material, while the other chemicals are used for protection, activation, and functionalization of the intermediate compounds. |
|
Preparation |
Synthesis of L-proline: Using glutamic acid as a raw material, it is esterified with absolute ethanol under the catalysis of sulfuric acid, and triethanolamine is added to free the aminosulfate to obtain glutamic acid-δ-ethyl ester. The glutamic acid-δ-ethyl ester is then reduced with a metal reducing agent potassium borohydride to obtain crude proline, which is finally separated and purified to obtain crude L-proline. |
|
benefits |
L-proline is considered a non-essential amino acid as it can be synthesised from arginine via the urea cycle in liver, and from glutamine/glutamic acid in the intestinal epithelium. It has a number of beneficial properties including connective tissue strengthening, Stronger Connective Tissue, Decreased Risk Of Heart Disease, Maintenance Of Muscle Tissueand skin health. |
|
Flammability and Explosibility |
Nonflammable |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
Proline is a cyclic, non-essential, hydrophobic amino acid. It is a proteinogenic amino acid which is crucial for primary metabolism. In peptide chains, proline residues confer structural constraints and enhance the susceptibility of proximal peptide bonds to protease activity. |
|
Purification Methods |
A likely impurity is hydroxyproline. Purify L-proline via its picrate which is crystallised twice from water, then decomposed with 40% H2SO4. The picric acid is extracted with diethyl ether, the H2SO4 in solution is precipitated with Ba(OH)2, and the filtrate is evaporated. The residue is crystallised from hot absolute EtOH [Mellan & Hoover J Am Chem Soc 73 3879 1951] or EtOH/Et2O. Its solubility in H2O is >100%. It sublimes at 182-187o/0.3mm with 99.4% recovery and unracemised [Gross & Gradsky J Am Chem Soc 77 1678 1955]. It is hygroscopic and is stored in a desiccator. [Greenstein & Winitz The Chemistry of the Amino Acids J. Wiley, Vol 3 pp 2178-2199 1961, Beilstein 22 III/IV 8, 22/1 V 31.] |
|
Structure and conformation |
L-proline, also known as L-pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid, is a neutral amino acid. Although proline is classified as an amino acid, it is strictly speaking an imino acid, since it contains an imino group (carbon-nitrogen double bond). Due to its cyclic pyrrolidine side chain it is classified as a nonpolar aliphatic amino acid. |
|
Role in Plant Physiology |
Metabolism and Growth: Important for maintaining plant metabolism and growth under abiotic stress conditions. |
|
Chemical Properties and Enzymatic Specificity |
Chirality: Proline exists as L and D enantiomers, with living cells predominantly metabolizing the L-proline form. |
|
Role in Human Proteome |
Concentration: L-Proline residues constitute nearly 6% of the human proteome, mainly found in L-Pro-rich proteins. |
|
Metabolic Functions |
Energy Source: Mitochondrial oxidation of proline provides ATP/energy for various cell types, including flight muscle cells, protozoan parasites, and cancer cells. |
|
Protective Effects and Cellular Functions |
ROS Protection: Protects human cells against ROS-mediated oxidative stress. |
|
Physical properties |
L-Proline, an amino acid, is odorless or has a slight, characteristic odor with a slightly sweet taste. It is synthesized from L-glutamine and L-glutamate via L-ornithine in intestine, and from L-ornithine in liver. It is widely used as an ingredient in infusion and infant formula. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: L-proline is pyrrolidine in which the pro-S hydrogen at position 2 is substituted by a carboxylic acid group. L-Proline is the only one of the twenty DNA-encoded amino acids which has a secondary amino group alpha to the carboxyl group. It is an essential component of collagen and is important for proper functioning of joints and tendons. It also helps maintain and strengthen heart muscles. It has a role as a micronutrient, a nutraceutical, an algal metabolite, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolite, an Escherichia coli metabolite, a mouse metabolite and a member of compatible osmolytes. It is a glutamine family amino acid, a proteinogenic amino acid, a proline and a L-alpha-amino acid. It is a conjugate base of a L-prolinium. It is a conjugate acid of a L-prolinate. It is an enantiomer of a D-proline. It is a tautomer of a L-proline zwitterion. |
|
General Description |
L-Proline is a non-essential amino acid. Peptides bond to proline, making it a useful building block for proteins. It can be used as a cell culture media component for the commercial biomanufacturing of therapeutic recombinant proteins and monoclonal antibodies.Pharmaceutical secondary standards for application in quality control, provide pharma laboratories and manufacturers with a convenient and cost-effective alternative to the preparation of in-house working standards. |
InChI:InChI=1/C5H9NO2/c7-5(8)4-2-1-3-6-4/h4,6H,1-3H2,(H,7,8)/t4-/m1/s1
Ten DL-Amino acids (AA), including neutr...
In search of novel protease inhibitors w...
Phosphonamidates which bear a simple res...
A new cyclopentapeptide dianthin I (1), ...
Parallel chemical and phylogenetic inves...
The structure of phosmidosine (1), a nov...
Two new peptides, stylissamides G and H,...
Captopril is a sulfur containing drug wh...
The heterogeneous asymmetric hydrogenati...
A new enzymatic process for the enantios...
Two new diketopiperazine derivatives, ba...
Hydroxyapatite-bound Pd catalyst was fou...
A new N-cinnamoyl tripeptide, designated...
An improved and practical approach to (R...
A family of 2,2-dimethyl-3-hydroxy-7-oct...
-
The species obtained by the reaction of ...
Two new bromopyrrole peptides, haloircin...
A 384-well microtitre plate fluorescence...
Aminopeptidase B (Ap-B) catalyzes the cl...
A novel cycloheptapeptide, tunicyclin A,...
The linear lipopeptides komesuamide (1) ...
The genus Centaurea L. (Asteraceae) is r...
The rates of racemization of optically a...
An acetylene-containing lipopeptide, jah...
A collection of the marine cyanobacteriu...
Cyclothiazomycin is a novel renin inhibi...
CXCR7 plays an emerging role in several ...
In addition to the four known stylissami...
-
Ionic liquids derived from prolinium est...
The solid-phase Horner-Emmons reaction w...
Chiral carbon nanoparticles (CCNPs) were...
-
Cyclo-(l-Pro-l-Met) was isolated from th...
Two new amino acid-sesquiterpene lactone...
The freshwater cyanobacterium Planktothr...
Malyngamide 3 (1) and cocosamides A (2) ...
We report 12 cyanobactin cyclic peptides...
-
A novel and sensitive method has been de...
Biseokeaniamides A, B, and C (1-3), stru...
Urumamide, a novel cyclic depsipeptide t...
-
The bioassay-guided fractionation of the...
Pitipeptolides A (1) and B (2) are cycli...
NMR-guided fractionation of a non-polar ...
Three new cyclic peptides, segetalins B,...
Reminiscent of signal transduction in bi...
As an alternative to the traditional che...
Four cyclic octapeptides, squamins C–F, ...
Amino acids are key synthetic building b...
Malaria remains a worldwide threat, affl...
Hoshinoamide C (1), an antiparasitic lip...
(S)-Pyrrolidine-1,2-dicarboxylic acid 1-[2-(4-methoxy-phenyl)-2-oxo-ethyl] ester

1-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethanone

L-proline
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
Irradiation; mild conditions;
|
(S)-N-(4-nitrophenyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide

4-nitro-aniline

L-proline
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With Tris-HCl buffer; an aminopeptidase from the seeds of Cannabis sativa; water; at 37 ℃; pH=7.5; Enzyme kinetics; Enzymatic reaction;
|
|
|
With MacIlvaine buffer; Patinopecten yessoensis mid-gut gland aminopeptidase; at 30 ℃; pH=7.0; Enzyme kinetics;
|
L-N-tosyl-proline
N-(3,5-dinitrobenzoyl)-L-proline
(S)-N-(naphthalen-2-yl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide
L-ornithine
Cbz-Pro-Pro-OH
1-[1-(toluene-4-sulfonyl)-L-prolyl]-L-proline
methyl (2S)-pyrrolidine carboxylate
(S)-acetylproline