Your Location:Home > Products > Textile chemicals > Carboxymethyl cellulose


CasNo: 9004-32-4
MF: C2H4O3.xNa.xUnspecified
Appearance: POWDER
|
Development and History |
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) was developed in Germany during World War I as a potential substitute for gelatin. However, technical challenges and high production costs delayed its full-scale commercialization at that time. |
|
Solubility and Tolerance to Salt |
CMC, being hydrophilic, can be salted out of solution with alkali metal salts. However, it is more tolerant to various types and concentrations of salt compared to other hydrocolloids like carrageenan, alginates, or pectin, which are sensitive to specific salts, such as calcium. |
|
Rheological Properties |
Upon complete dissolution, CMC exhibits several useful rheological properties, making it valuable in various applications. It stabilizes and thickens variegated sauces and ribbon ties used in ice cream preparations. It also interacts with bakery ingredients to enhance functional performance. |
|
Effect on Glucose Metabolism and Lipid Homeostasis |
Tadalafil does not significantly affect lipid homeostasis or body composition, as demonstrated by studies showing no change in body mass index (BMI) or adipose tissue levels. |
|
Oral Drug Delivery |
CMC, as a polyanionic biopolymer, is widely used in oral drug delivery systems. Its high pH sensitivity makes it suitable for site-specific drug delivery applications. |
|
Biodegradability and Non-Toxicity |
CMC is a derivative of natural cellulose, making it biodegradable, flexible, and non-toxic. It is known for its ability to form membranes with good barrier function and amphiphilicity. |
|
Improvement of Film Properties |
CMC, when combined with cassava starch (CS), improves the physical and chemical properties of edible films. This combination enhances membrane formation, barrier function, and flexibility, making it suitable for food packaging applications. Studies have shown that CS and CMC blend films can prolong the shelf life of perishable food items like bananas by incorporating lactic acid bacteria. |
|
description |
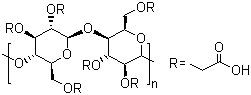
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose is a water-soluble polymer. As a solution in water, it has thixotropic properties. It is useful in helping to hold the components of pyrotechnic compositions in aqucous suspension (e.g., in the making of black match). It is also an especially effective binder that can be used in small amounts in compositions, where the binder can intcrfere with the intended effect (e.g., in strobe compositions). However, its sodium content obviously precludes its use in most color compositions. Sodium carboxymethyl-cellulose is manufactured from cellulose by various proccsses that replacc some of the hy drogen atoms in the hydroxyl[OH] groups of the cellulose molecule with acidic carboxymethyl [-CH2CO.OH] groups,which are neutralized to form the corresponding sodium salt. Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose is white when pure; industrial grade material may be grayish-white or cream granules or powder. |
|
Product Features |
Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) is tackifier, at room temperature, it is non-toxic tasteless white flocculent powder, it is stable and soluble in water, aqueous solution is neutral or alkaline transparent viscous liquid, it is soluble in other water-soluble gums and resins, it is insoluble in organic solvents such as ethanol. Carboxymethyl cellulose is the substituted product of cellulosic carboxymethyl group. According to their molecular weight or degree of substitution, it can be completely dissolved or insoluble polymer, the latter can be used as the weak acid cation of exchanger to separate neutral or basic proteins. Carboxymethyl cellulose can form highly viscous colloidal solution with adhesive, thickening, flowing, emulsifying, shaping, water, protective colloid, film forming, acid, salt, suspensions and other characteristics, and it is physiologically harmless, so it is widely used in the food, pharmaceutical, cosmetic, oil, paper, textiles, construction and other areas of production. |
|
Synthesis |
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose is formed when cellulose reacts with mono chloroacetic acid or its sodium salt under alkaline condition with presence of organic solvent, hydroxyl groups substituted by Sodium carboxymethyl groups in C2, C3 and C6 of glucose, which substitution slightly prevails at C2 position.Generally, there are two steps in manufacturing process of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, alkalinization and etherification.Step 1: AlkalinizationDisperse the raw material cellulose pulp in alkali solution (generally sodium hydroxide, 5–50%) to obtain alkali cellulose.Cell-OH+NaOH →Cell·O-Na+ +H2OStep 2: EtherificationEtherification of alkali cellulose with sodium monochloroacetate (up to 30%) in an alcohol-water medium. The mixture of alkali cellulose and reagent is heated (50–75°C) and stirred during the process.ClCH2COOH+NaOH→ClCH2COONa+H2OCell·O-Na+ +ClCH2COO- →Cell-OCH2COO-NaThe DS of the sodium CMC can be controlled by the reaction conditions and use of organic solvents (such as isopropanol).https://www.longdom.orghttps://foodadditives.net |
|
Usage Instruction |
Use warm water or cold water when preparing the solution, and stir till it completely melts. The amout of added water depends on variety and the use of multiple requirements. High viscosity sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (HV-CMC) is a white or slightly yellow fibrous powder, hygroscopic, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, easy to ferment, insoluble in acids, alcohols and organic solvents, easily dispersed to form colloidal solution in water. It is reacted by the acid and fibrous cotton, it is mainly used for water-based drilling fluids tackifier, it has certain role of fluid loss, it has strong salt and temperature resistance especially. |
|
Production Methods |
Alkali cellulose is prepared by steeping cellulose obtained from wood pulp or cotton fibers in sodium hydroxide solution. The alkaline cellulose is then reacted with sodium monochloroacetate to produce carboxymethylcellulose sodium. Sodium chloride and sodium glycolate are obtained as by-products of this etherification. |
|
Definition |
A semisynthetic, water-soluble polymer in which CH 2 COOH groups are substituted on the glucose units of the cellulose chain through an ether link- age. Mw ranges from 21,000 to 500,000. Since the reaction occurs in an alkaline medium, the prod- uct is the sodium salt of the carboxylic acid R-O- CH 2 COONa. |
|
General Description |
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) belongs to the class of anionic linear structured cellulose. Its components consist of polysaccharide composed of fibrous tissues of plants. It is a water soluble polymer which can be used as a polyelectrolyte cellulose derivative. |
|
Pharmaceutical Applications |
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (NaCMC) is the sodium salt of carboxymethyl cellulose, an anionic derivative.It is widely used in oral and topical pharmaceutical formulations, primarily for its viscosity-increasing properties. Viscous aqueous solutions are used to suspend powders intended for either topical application or oral and parenteral administration. Carboxymethylcellulose sodium may also be used as a tablet binder and disintegrant, and to stabilize emulsions.Higher concentrations, usually 3–6%, of the medium-viscosity grade are used to produce gels that can be used as the base for applications and pastes; glycols are often included in such gels to prevent them drying out. Carboxymethylcellulose sodium is also used in self-adhesive ostomy, wound care, and dermatological patches as a muco-adhesive and to absorb wound exudate or transepidermal water and sweat. This muco-adhesive property is used in products designed to prevent post-surgical tissue adhesions; and to localize and modify the release kinetics of active ingredients applied to mucous membranes; and for bone repair. Encapsulation with carboxymethylcellulose sodium can affect drug protection and delivery. There have also been reports of its use as a cyto-protective agent.Carboxymethylcellulose sodium is also used in cosmetics, toiletries, surgical prosthetics, and incontinence, personal hygiene, and food products. |
|
Safety Profile |
Mildly toxic by ingestion. Experimental reproductive effects. Questionable carcinogen with experimental neoplastigenic data. It migrates to food from packagmg materials. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NazO. See also POLYMERS, SOLUBLE. |
|
Safety |
Carboxymethylcellulose sodium is used in oral, topical, and some parenteral formulations. It is also widely used in cosmetics, toiletries, and food products, and is generally regarded as a nontoxic and nonirritant material. However, oral consumption of large amounts of carboxymethylcellulose sodium can have a laxative effect; therapeutically, 4–10 g in daily divided doses of the medium- and high-viscosity grades of carboxymethylcellulose sodium have been used as bulk laxatives. The WHO has not specified an acceptable daily intake for carboxymethylcellulose sodium as a food additive since the levels necessary to achieve a desired effect were not considered to be a hazard to health. However, in animal studies, subcutaneous administration of carboxymethylcellulose sodium has been found to cause inflammation, and in some cases of repeated injection fibrosarcomas have been found at the site of injection. Hypersensitivity and anaphylactic reactions have occurred in cattle and horses, which have been attributed to carboxymethylcellulose sodium in parenteral formulations such as vaccines and penicillins. LD50 (guinea pig, oral): 16 g/kg LD50 (rat, oral): 27 g/kg |
|
storage |
Carboxymethylcellulose sodium is a stable, though hygroscopic material. Under high-humidity conditions, carboxymethylcellulose sodium can absorb a large quantity (>50%) of water. In tablets, this has been associated with a decrease in tablet hardness and an increase in disintegration time. Aqueous solutions are stable at pH 2–10; precipitation can occur below pH 2, and solution viscosity decreases rapidly above pH 10. Generally, solutions exhibit maximum viscosity and stability at pH 7–9. Carboxymethylcellulose sodium may be sterilized in the dry state by maintaining it at a temperature of 1608℃ for 1 hour. However, this process results in a significant decrease in viscosity and some deterioration in the properties of solutions prepared from the sterilized material. Aqueous solutions may similarly be sterilized by heating, although this also results in some reduction in viscosity. After autoclaving, viscosity is reduced by about 25%, but this reduction is less marked than for solutions prepared from material sterilized in the dry state. The extent of the reduction is dependent on the molecular weight and degree of substitution; higher molecular weight grades generally undergo a greater percentage reduction in viscosity. Sterilization of solutions by gamma irradiation also results in a reduction in viscosity. Aqueous solutions stored for prolonged periods should contain an antimicrobial preservative. The bulk material should be stored in a well-closed container in a cool, dry place. |
|
Properties and Applications |
TEST ITEMS SPECIFICATION CMC-LV CMC-HV Appearance Cream colored and free flowing powder Cream colored and free flowing powder Degree of Substitution 0.6-0.9 0.6-0.9 pH 6-9 6-9 Moisture % 10% max 10% max Sodium CMC content on dry basis 70% min 70% min Viscosity at 600RPM 90 max in deionized water 10 max 4% salt water mud,API water loss 30 max in deionized water 30 min in 4% salt water 30 min in 4% saturated salt water 10 max 4% salt water mud,API water loss |
|
TEST ITEMS |
SPECIFICATION |
|
CMC-LV |
CMC-HV |
|
Appearance |
Cream colored and free flowing powder |
|
Degree of Substitution |
0.6-0.9 |
|
pH |
6-9 |
|
Moisture % |
10% max |
|
Sodium CMC content on dry basis |
70% min |
|
Viscosity at 600RPM |
90 max in deionized water 10 max 4% salt water mud,API water loss |
|
Purification Methods |
Dialyse it for 48hours against distilled water and freeze-dry if a solid is required. |
|
Incompatibilities |
Carboxymethylcellulose sodium is incompatible with strongly acidic solutions and with the soluble salts of iron and some other metals, such as aluminum, mercury, and zinc. It is also incompatible with xanthan gum. Precipitation may occur at pH < 2, and also when it is mixed with ethanol (95%). Carboxymethylcellulose sodium forms complex coacervates with gelatin and pectin. It also forms a complex with collagen and is capable of precipitating certain positively charged proteins. |
|
Regulatory Status |
GRAS listed. Accepted as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (dental preparations; intraarticular, intrabursal, intradermal, intralesional, and intrasynovial injections; oral drops, solutions, suspensions, syrups and tablets; topical preparations). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Nonmedicinal Ingredients. |
InChI:InChI=1/C6H12O6.C2H4O2.Na/c7-1-3(9)5(11)6(12)4(10)2-8;1-2(3)4;/h1,3-6,8-12H,2H2;1H3,(H,3,4);